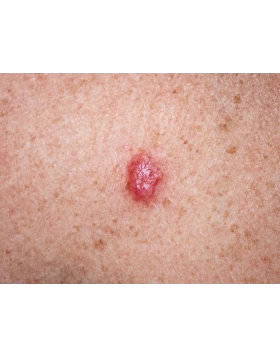
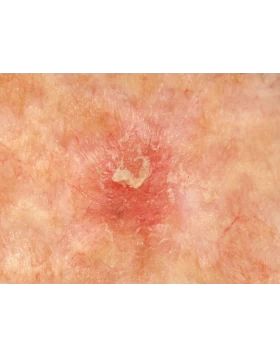
Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is a type of skin cancer that develops in the cells of the epidermis and often occurs in areas that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, neck and hands. It usually presents as a rapidly growing sore, nodule or crust that does not heal. Early diagnosis and treatment is critical to preventing cancer from spreading to other parts of the body. The choice of treatment depends on the size, location and stage of the cancer, with options including surgical removal, cryotherapy or local treatments.

Do you have additional questions about the service?
What are the risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma?
Major risk factors include prolonged sun exposure, light skin color, advanced age, radiation history, and use of light-colored or weak sunscreens.
What are the main symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma?
Symptoms include sores that won't heal, red bumps, scaly surfaces, or areas that bleed easily.
Is squamous cell carcinoma dangerous?
If left untreated, squamous cell carcinoma can spread to other parts of the body, so it's important to get it diagnosed and treated early.
What treatments are available for squamous cell carcinoma?
Treatments include surgical removal, cryotherapy, and other approaches depending on the size, location, and stage of the carcinoma.


 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά